This installation guide is intended for the Super Famicom/SNES Jr. and covers capacitor replacement, as well as the simultaneous installation of the SNES RGB and SNES AIO. When installing both kits together, specific steps must be followed, as the process deviates from the original individual guides.
Please click here if you wish to purchase a capacitor kit, here if you wish to purchase a SNES RGB bypass kit or here if you wish to purchase a SNES AIO kit.
Contents
Please click below to skip to each section.
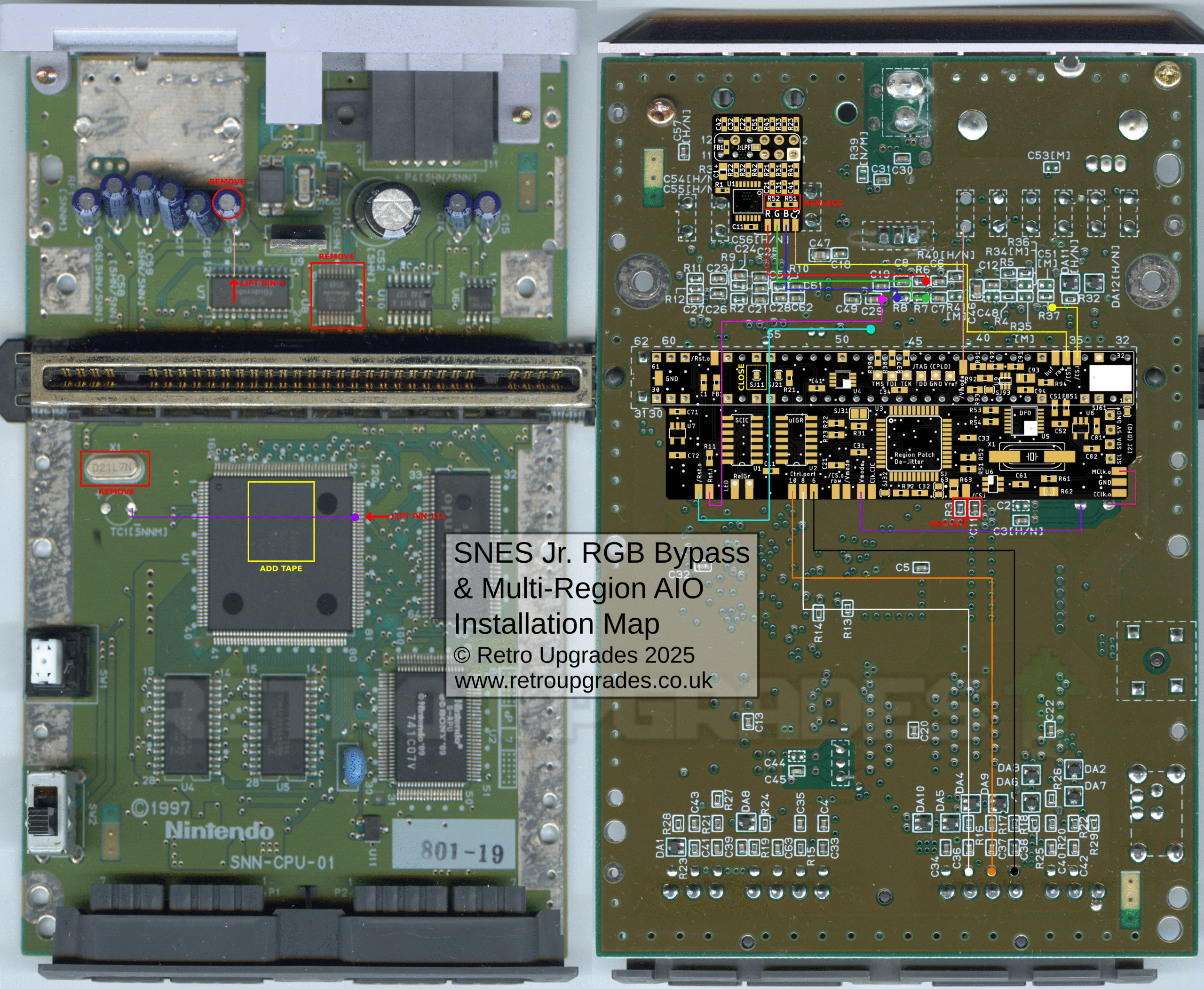
1.0 – Super Famicom Jr. SNN-CPU-01 Quick Install Map
2.0 – Full Installation Guide
2.1 – Capacitor Replacement
2.2 – SNES RGB Bypass
2.3.1 – SNES Multi-Region AIO Component Removal
2.3.2 – SNES Multi-Region AIO Installation of PCB
2.3.3 – SNES Multi-Region AIO Connections
2.3.4 – SNES Multi-Region AIO Jumpers
1.0 – Quick Install Map
Please click here for the full size image (opens in a new tab). Caution: large image file size.
2.0 – Full Installation Guide
2.1 – Capacitor Replacement
Using our SNN-CPU-01 capacitor replacement guide here, start by removing the capacitors.
Important: Leave original capacitor ‘C9’ populated. It will be removed later so replacing it is unnecessary.
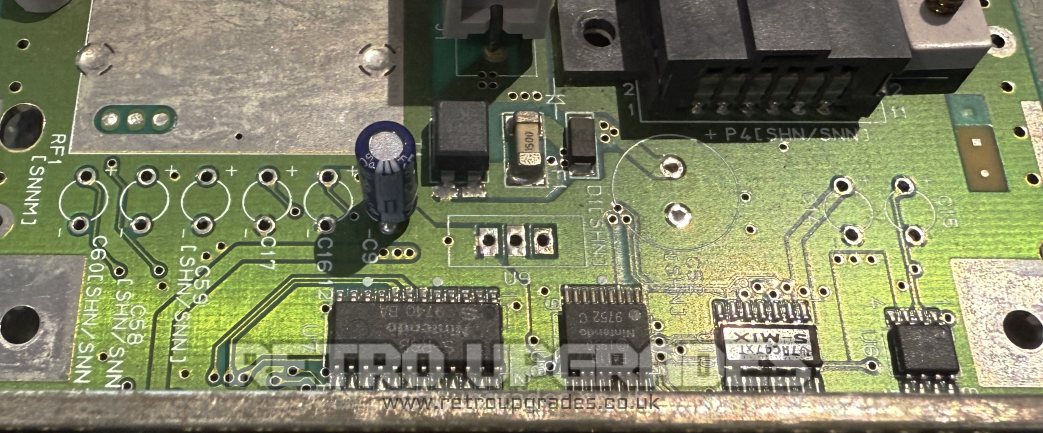
Once the capacitors and voltage regulator have been replaced, test the console to ensure operation is normal.
Optional: if your console experiences the vertical line issue, replace ‘C61’ on the bottom side with the capacitor provided with your capacitor replacement kit. See here.
2.2 – SNES RGB Bypass
For this step, we’ll follow Tzorrimahm’s original guide here, but with some minor install point changes. Firstly, RGB will be pulled from elsewhere on the bottom side of the board as shown.
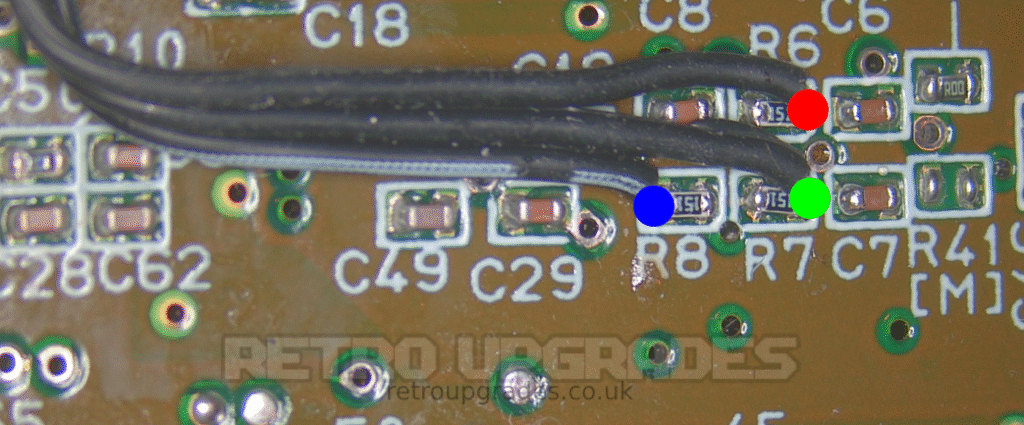
‘R’ on the SNES RGB bypass board to the right side of ‘R6’.
‘G’ on the SNES RGB bypass board to the right side of ‘R7’.
‘B’ on the SNES RGB bypass board to the left side of ‘R8’.
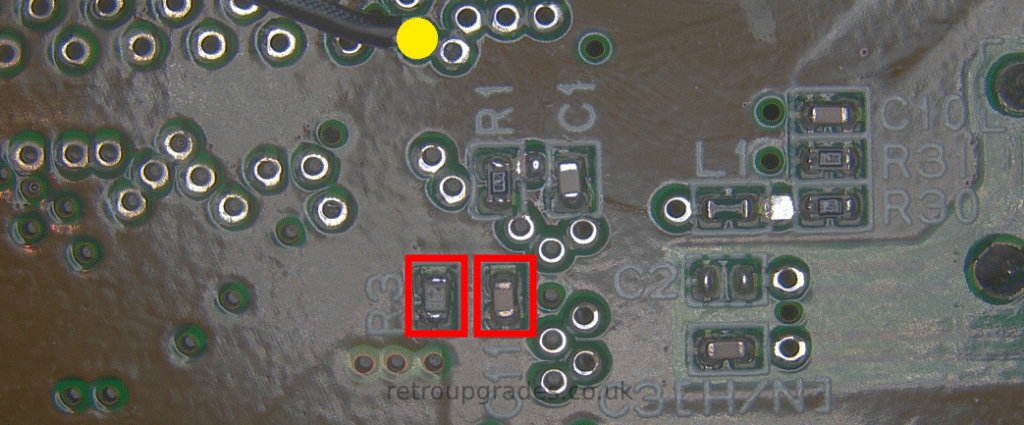
‘CS’ on the SNES RGB bypass board to the via highlighted (same as Tzorrimahm’s guide).
‘R3′ must be replaced with the brightness fix resistor included with the SNES RGB kit.
Optional: Replace ‘C11’ with the ghosting fix capacitor included with your SNES RGB kit. The console can be tested first and we only recommend to replace ‘C11’ if you are experiencing any ghosting.
Test the console to ensure operation is normal. The console should now output RGB.
After confirming successful operation, remove the sync wire completely or put it to the side. Once the AIO kit is installed, sync will be wired differently. The purpose of wiring sync previously was simply to test the RGB kit install.
2.3.1 – SNES Multi-region AIO – Component Removal
After successfully installing the SNES RGB kit and removing the sync wire, it’s time to install the SNES AIO kit.
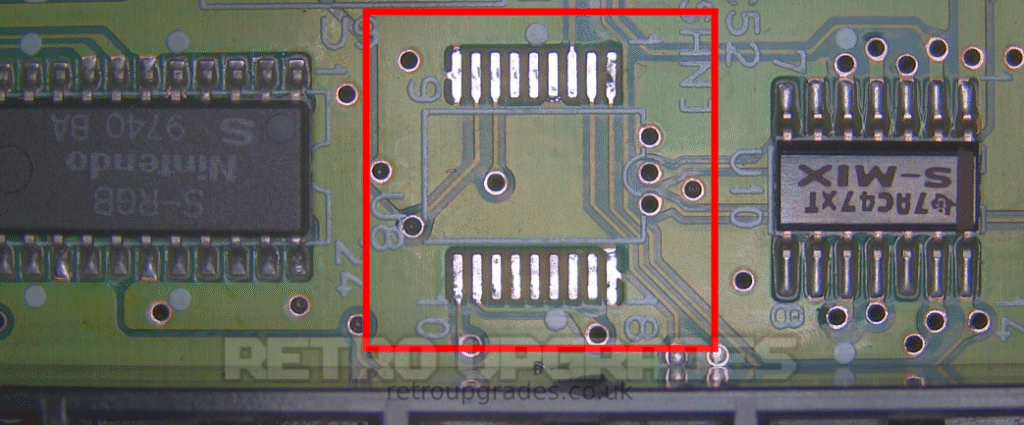
Remove the CIC-lock ‘U8’ which is located above the cartridge connector and between the S-RGB and S-MIX chips.
Optional: You can also lift pins 1, 2, 10 and 11, but removing it makes wire routing easier in future steps, so this guide will assume it has been removed.
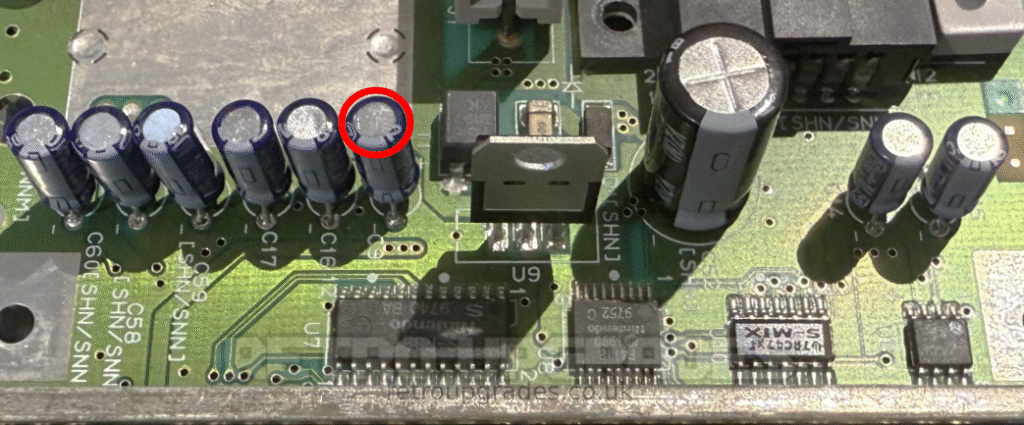
Remove ‘C9’ as ‘U8’ has been removed.
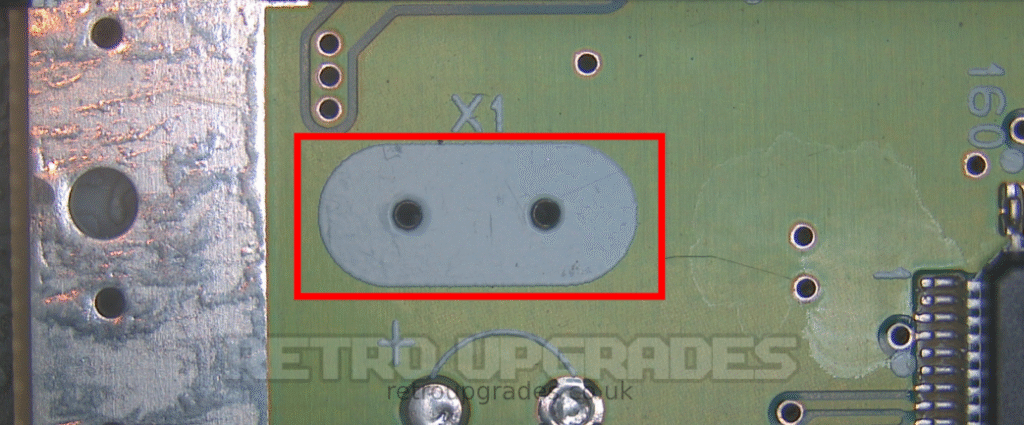
Remove X1.
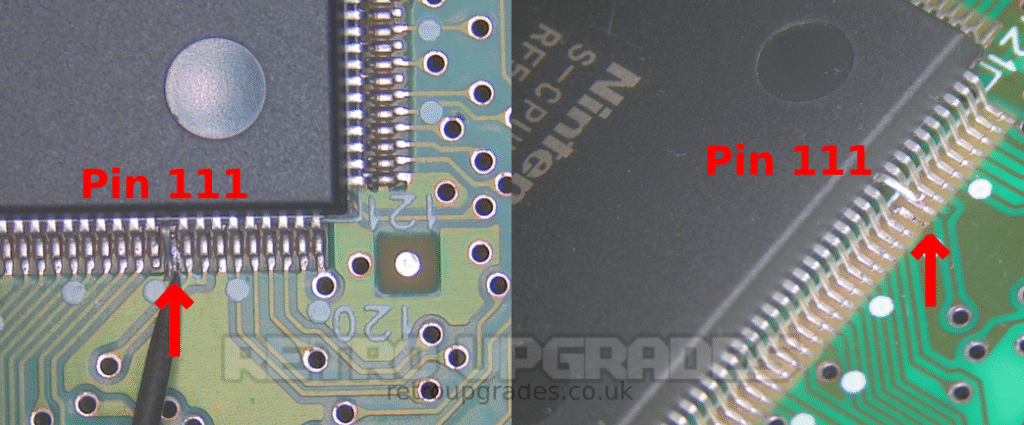
Lift S-CPUN pin 111.
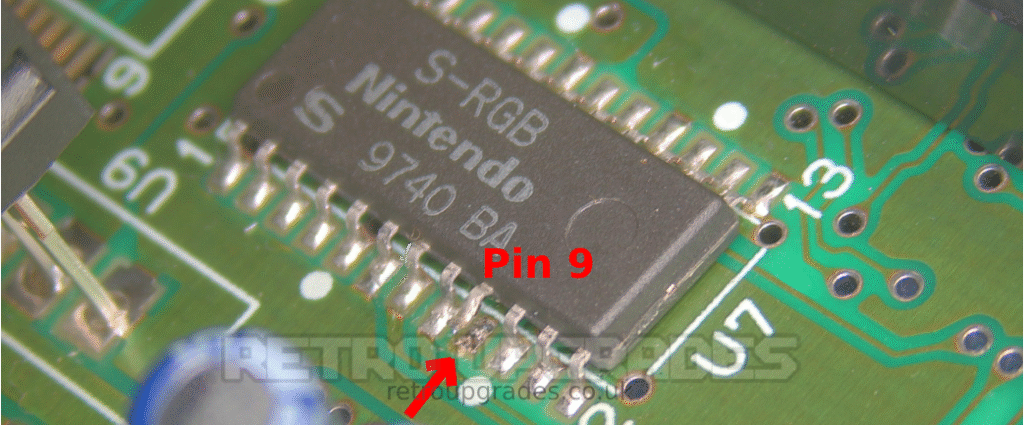
Lift S-RGB pin 9.
2.3.2 – SNES Multi-region AIO – Installation of the PCB
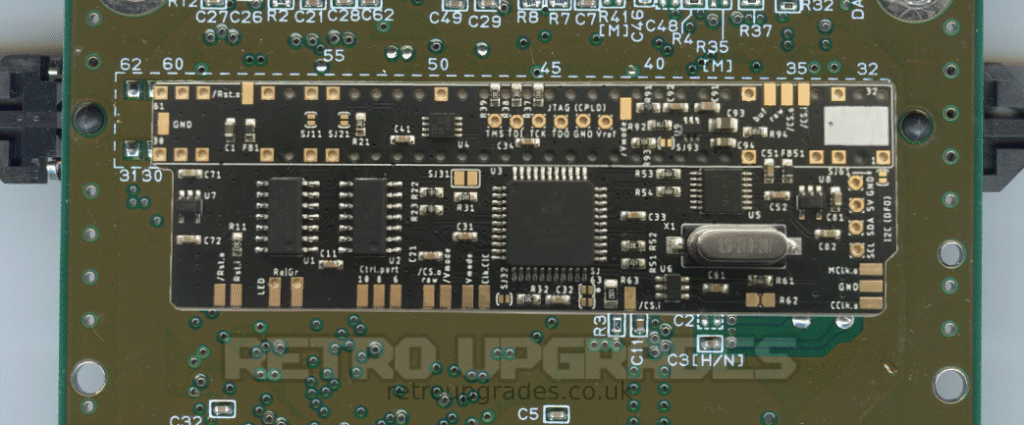
Align the AIO board to the cartridge slot pins on the bottom side of the SNES. The pin markings must match. Beware of orientation!
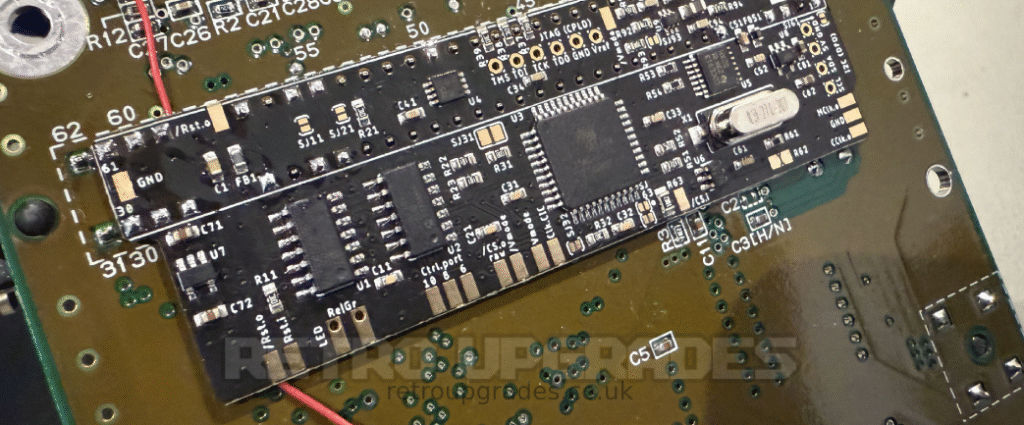
Run one strand of 30AWG wire, approximately 10 centimeters long, underneath the left side of the PCB which will be used for the Reset In connection. Leave it free for now. Doing this step now will makes it far easier than trying to slide it under after the PCB has been soldered into place.
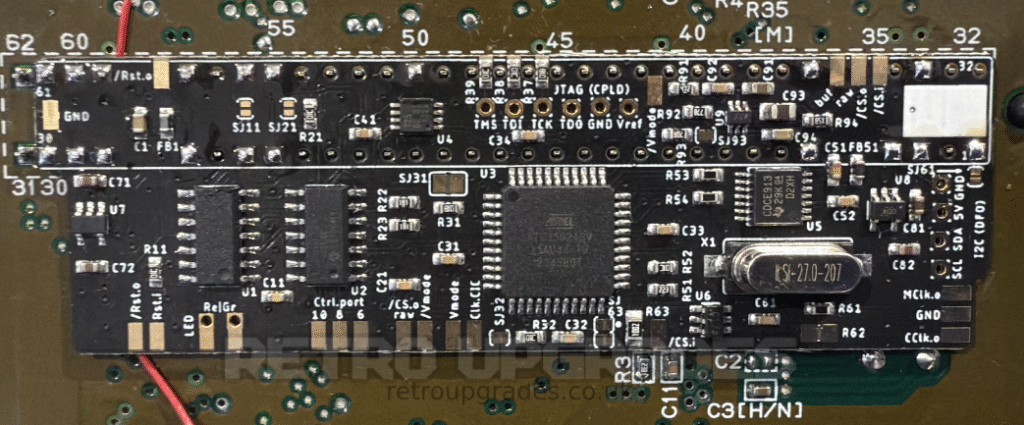
Solder the PCB to the top of the slot pins and ensure there is a small gap between the SNES mainboard and SNES AIO board. The 30AWG wire from the previous step helps act as a spacer. Alternatively, the bottom side of the AIO board can be isolated with tape.
Important: All connections must be well flowed. Pin ‘5’ and pin ’36’ may need more power due to the higher thermal mass of the GND plane.
2.3.3 – SNES Multi-region AIO – Connections
Please feel free to cross-reference with the quick install map as it provides a clear overview of the board.
Click here for the quick install map (opens in a new tab). Caution: large image file size.
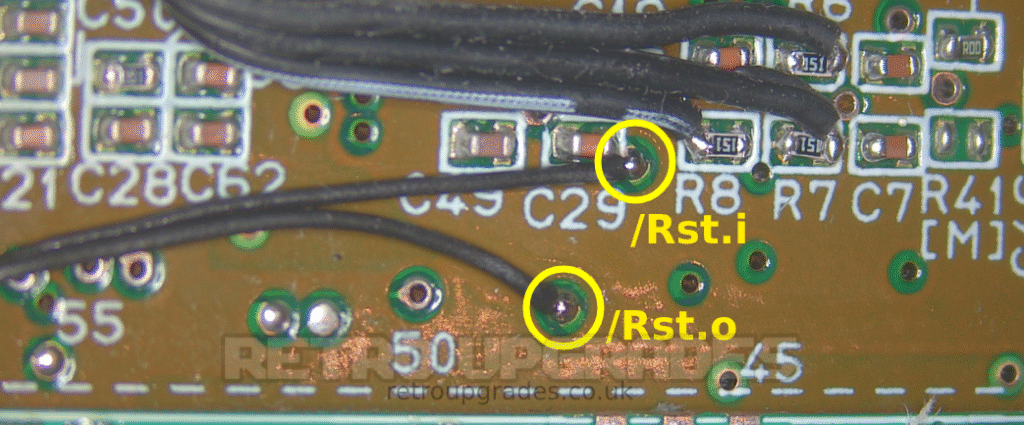
Using the 30AWG wire we routed underneath the board in the previous step, connect ‘Rst.i’ on the AIO board to the right side of ‘C29’.
Connect the upper ‘/Rst.o’ pad on the AIO board to the via immediately below ‘C29’.
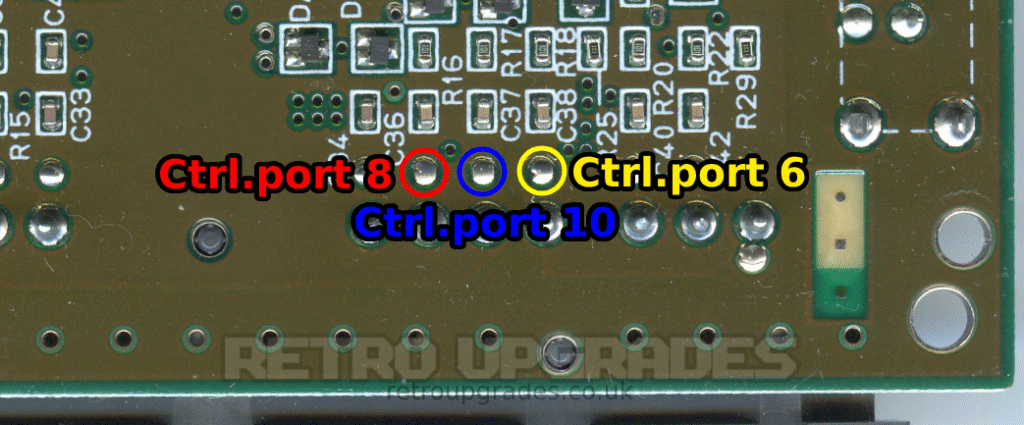
Connect the ‘Ctrl.port 10’ to controller one pin ‘3’.
Connect the ‘Ctrl.port 8’ to controller one pin ‘2’.
Connect the ‘Ctrl.port 6’ to controller one pin ‘4’.
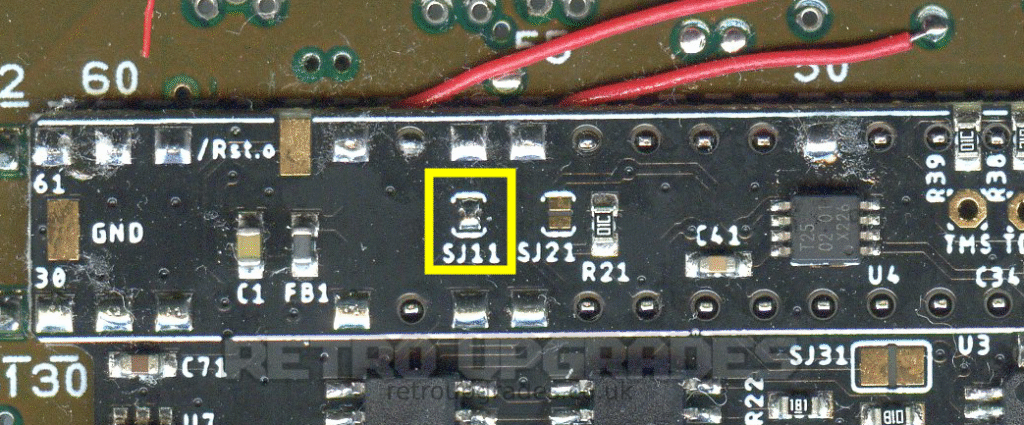
Close jumper ‘SJ11’.
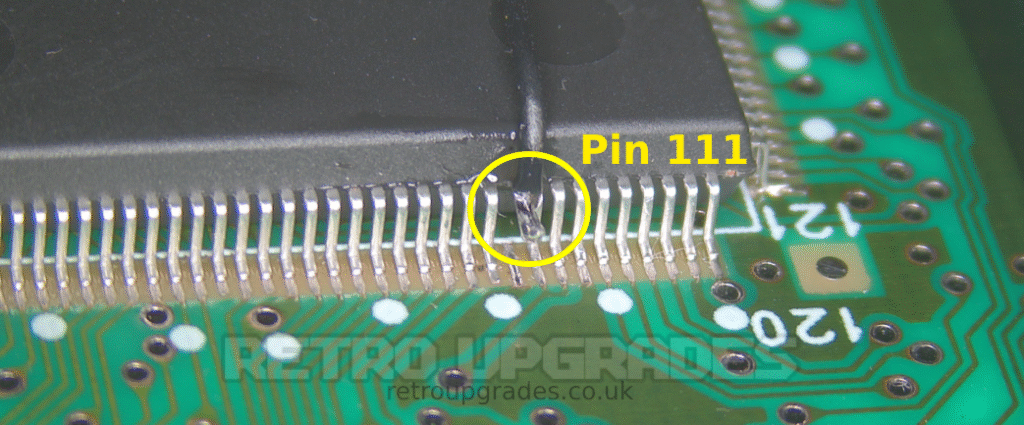
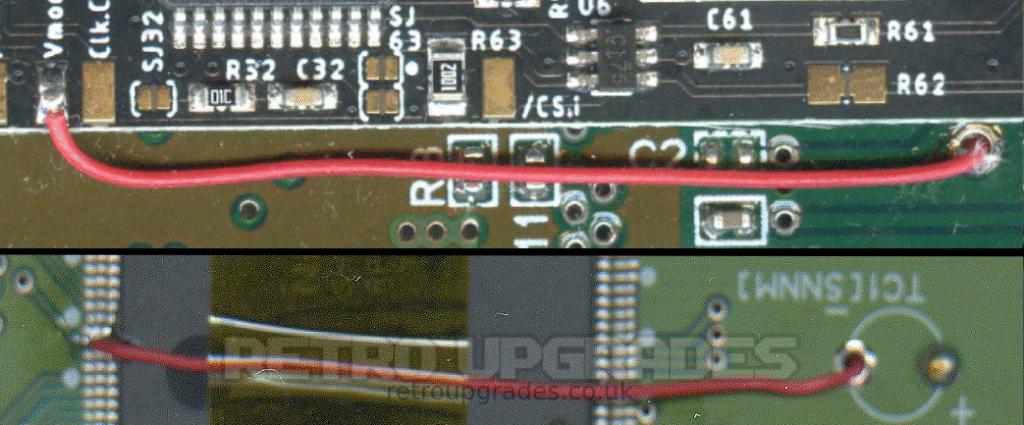

Connect the ‘Vmode’ pad (NOT /Vmode) on the AIO board to lifted pin 111 of the S-CPUN. Route the 30AWG wire through ‘TC1’ for a clean result. Place some kapton tape on the top of S-CPUN to help act as strain relief.
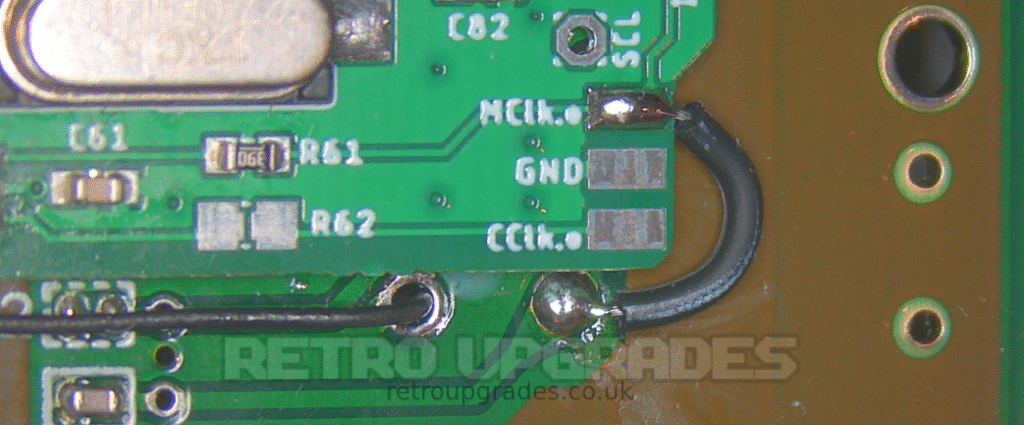
Connect ‘MCLK.o’ to ‘X1’ (the right side which connects to S-CPUN pin 9).
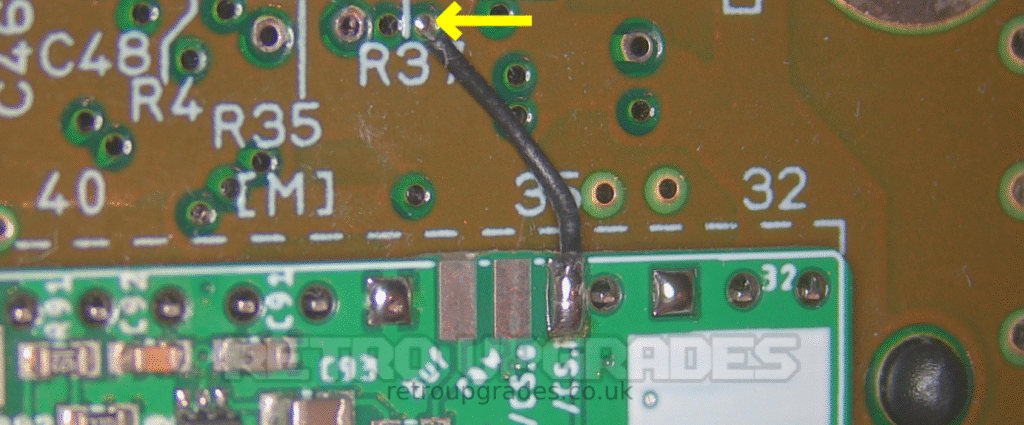
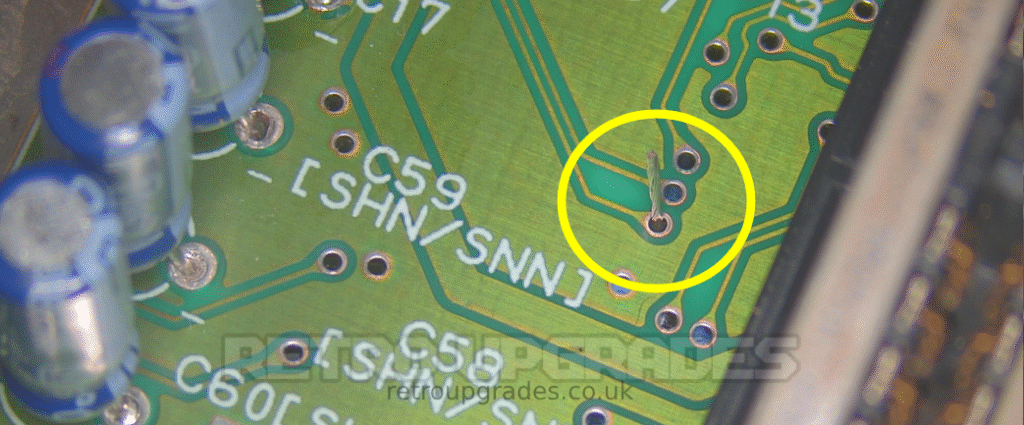
Connect ‘/CS.i’ (sync in) pad on the AIO board to the via shown above ‘R37’ (which connects to pad 7 of the S-RGB). Trim the wire so that a long end is exposed and thread it through the via. Solder it on the top side and trim.
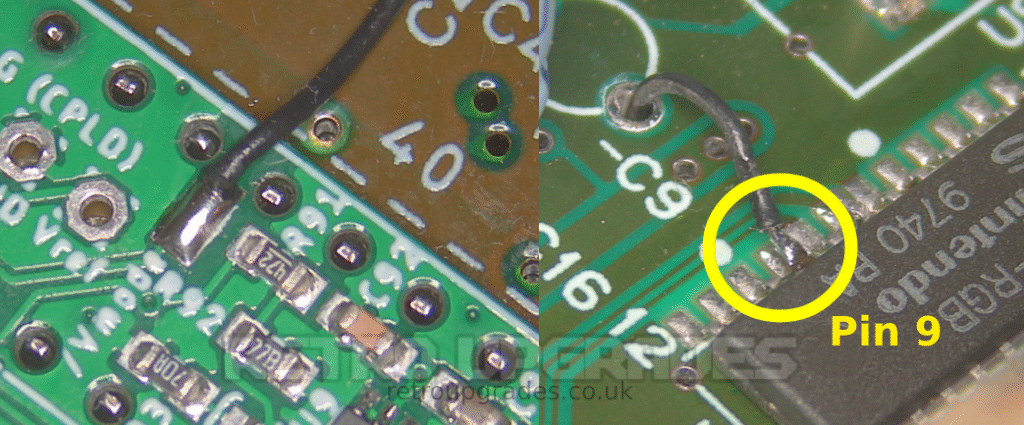
Connect the upper ‘/Vmode’ pad to lifted pin 9 of the S-RGB. Route this wire through the empty hole for capacitor ‘C9’ for a clean result.
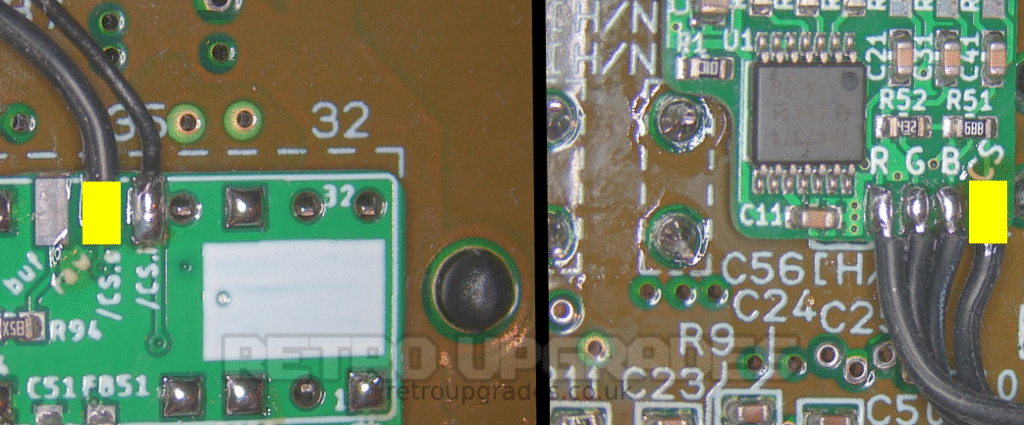
Connect the ‘/CS.o raw’ (TTL csync out) pad on the AIO board to the ‘CS’ pad on the SNES RGB board.
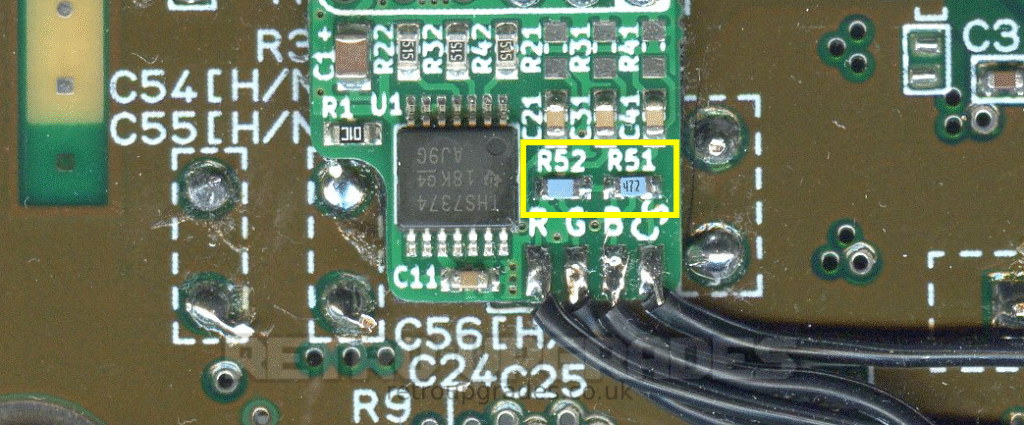
Lastly, when both kits are installed, two resistor values on the SNES RGB bypass board need to be changed. These resistors are included if both kits are purchased from us in the same order.
‘R51′ must be replaced with a ‘4.7kΩ 0603′ resistor.
‘R52′ must be replaced with a ‘10.7kΩ 0603’ resistor.
2.3.4 – SNES Multi-region AIO – Jumpers
We typically only close ‘SJ11’ and ‘SJ31’ which are for alt. SuperCIC clock & dejitter disable. That’s it.
Optional: depending on your setup, you may wish to configure other jumpers.
- ‘SJ11’: Alternative clock for the SuperCIC. Close this jumper if you don’t connect the Clk.CIC pad in order to use the clock meant for the CIC key.
- ‘SJ21’: Close this jumper if you use an LED with a common anode. Otherwise, leave this jumper untouched.
- ‘SJ31’: Closing this jumper permanently disables the DeJitter function. This solder jumper is slightly larger to give the installer the option to connect a slide switch here (speed-runner discussions). We recommend keeping DeJitter off unless you are using the OSSC or are experiencing issues getting a stable picture.
- ‘SJ32’: Short this jumper if the board is installed in a non-1Chip SNES. (Note: SNES Jr. / SNES2 are also 1Chip models.)
- ‘SJ61’: Distributes clock output to cartridge slot pin 1. Do not close this jumper on 1Chip SNES units. Note: If SJ32 is open, SJ61 must also be open.
- ‘SJ63’: Determines which color carrier is forwarded to output. This jumper has two options. Do not close both!
- ‘SJ63.1’: (marked with a dot): Outputs color carrier derived from non-DeJittered clock. Use this if you experience discoloration on composite video or S-Video (see related discussion thread at shmups).
This is the default for all earlier versions of the mod board flashed with the current firmware. To use the other color carrier, revert to a previous firmware version. - ‘SJ63.2’: Outputs color carrier derived from the DeJittered clock. (We personally need to use this, as our TV does not like the color carrier from the non-DeJittered clock.)
Important: You must not close both jumpers! - ‘SJ93: Controls the sync level of buffered CSYNC output.
- Open: ~1.87V @ 75Ω termination (Most common).
Requires a resistor inside the sync wire to further attenuate the signal. Designed for cables with a 470Ω resistor, resulting in ~450mV @ 75Ω. - Closed: ~300mV @ 75Ω termination.
Suitable for pass-through wired sync cables. Works with standard TV/scaler setups.
Troubleshooting:
If any noticeable flickering is present whilst using composite video or s-video, please see here for a fix or alternatively disable dejitter with ‘SJ31’. The component designators and values on the SNES Jr. are the same.
When using an Everdrive, if there are a few lines missing from the top of the picture, it is due to the ghosting capactitor. Either adjust the value between 220nF-470nF or adjust the “1 CHIP transient fixes” setting in the Everdrive menu.
